The state of mental health research in adolescents and youth, especially in contexts of limited resources, is mapped illustrated in the ontological framework.
Ontology
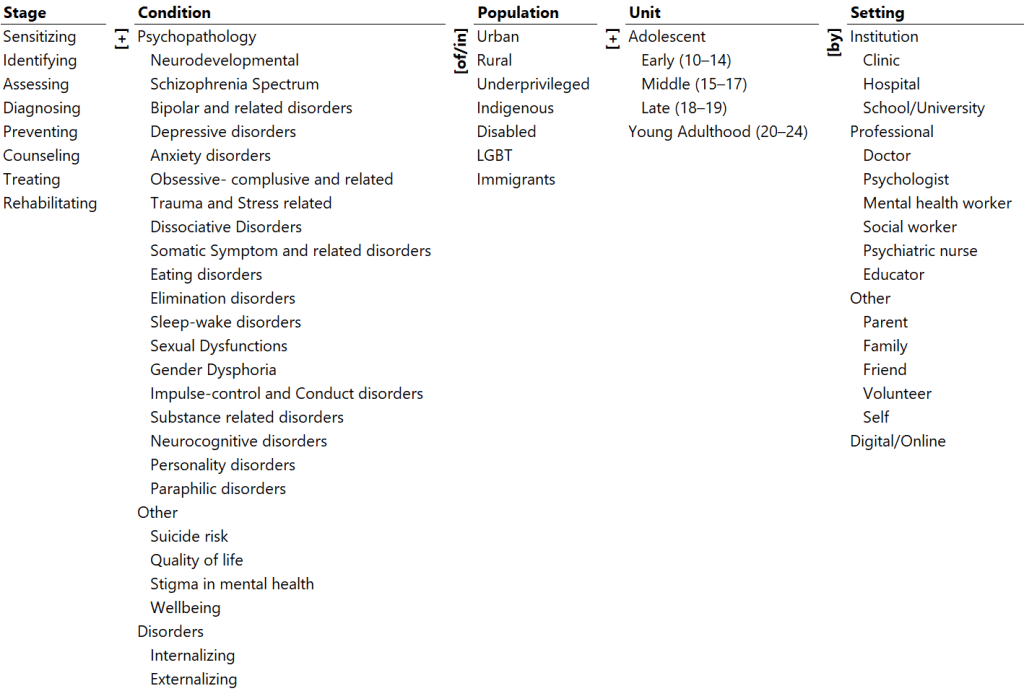
Illustrative Pathways
- Treating depressive disorders in urban youth by psychologist.
- Identifying suicide risk in underprivileged middle adolescents by school.
- Preventing substance-related disorders in rural late adolescents by parent.
Glossary
- Stage: The stage of mental healthcare.
- Sensitizing: Sensitization about adolescent and adult mental health issues and wellbeing.
- Identifying: Identification of mental health issues and wellbeing.
- Assessing: Assessment of mental health issues and wellbeing.
- Diagnosing: Diagnosis of mental health issues and wellbeing.
- Preventing: Prevention of mental health issues and wellbeing.
- Counselling: Counselling for mental health issues and wellbeing.
- Treating: Treatment for mental health issues and wellbeing.
- Rehabilitating: Rehabilitation measures for mental healthcare and wellbeing.
- Condition: The condition of mental health
- Psychopathology*: Psychopathological conditions.
- Neurodevelopmental: Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of conditions with the onset in the development period. It includes intellectual development disorder (earlier called mental retardation or intellectual disability), communication disorders, autism spectrum disorder, motor disorders, specific learning disorders and ADHD.
- Schizophrenia Spectrum: Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders that include delusional disorder, schizotypal (personality) disorder, schizoaffective disorder and catatonia.
- Bipolar and related disorders: It includes bipolar I disorder, bipolar II disorder, bipolar disorder NED (not elsewhere defined) and Major depressive disorder.
- Depressive disorders: It includes Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder (DMDD) which is observed in children up to the age of 18 years, and persistent depressive disorder (earlier called as dysthymia).
- Anxiety disorders: It includes various forms of phobias and anxiety disorders (social anxiety disorder, separation anxiety, and selective mutism), panic disorder, agoraphobia.
- Obsessive- compulsive and related: It includes disorders like excoriation (skin-picking) disorder, hoarding disorder, substance-/medication-induced obsessive-compulsive and related disorder, and obsessive-compulsive and related disorder due to another medical condition.
- Trauma and Stress related: it includes PTSD, acute stress disorder, reactive attachment disorder and disinhibited social engagement disorder.
- Dissociative Disorders: It includes disorders like depersonalization/derealization, dissociative fugue, dissociative identity disorder.
- Somatic Symptom and related disorders: It includes somatic symptom disorder- which is a mental disorder that manifests as physical symptoms that suggest illness but cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition.
- Eating disorders: It includes disorders like pica, rumination disorder, binge eating disorder, bulimia nervosa, anorexia nervosa, avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder.
- Elimination disorders: Elimination disorders occur when children who are otherwise old enough to eliminate waste appropriately repeatedly void feces or urine in inappropriate places or at inappropriate times. The two disorders that fall under this category are Enuresis and Encopresis.
- Sleep-wake disorders: It includes insomnia disorder, narcolepsy, hypersomnolence, obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea, central sleep apnea, and sleep-related hypoventilation, circadian rhythm sleep wake disorders, Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and restless legs syndrome.
- Sexual Dysfunctions: It includes female sexual interest/arousal disorder, and genito pelvic pain disorder.
- Gender Dysphoria: It is disorder that is caused by a distress a person feels due to a mismatch between their gender identity—their personal sense of their own gender—and their sex assigned at birth.
- Impulse-control and Conduct disorders: It includes oppositional defiant disorder; conduct disorder; and disruptive behavior disorder not otherwise specified became other specified and unspecified disruptive disorder, impulse-control disorder, and conduct disorders, intermittent explosive disorder, pyromania, kleptomania, and Anti-Social Personality Disorder (ASPD).
- Substance related and Addictive disorders: These include substance abuse disorders, gambling disorder, and tobacco use disorder.
- Neurocognitive disorders: It includes major dementia, amnestic disorder, and delirium.
- Personality disorders: These are a class of mental disorders characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts. It includes disorders like paranoid personality disorder, schizoid personality disorder, schizotypal personality disorder, ASPD, borderline personality disorder, histrionic personality disorder, narcissistic personality disorder, avoidant personality disorder, dependent personality disorder and obsessive-compulsive personality disorder.
- Paraphilic disorders: Formerly named perversions, the experience of intense sexual arousal to atypical objects, situations, fantasies, behaviors, or individuals, e.g.: Pedophilic disorder.
- Other: Other conditions.
- Suicide risk: Likelihood for an individual to attempt or die by suicide.
- Quality of life (QOL): QOL is the degree to which an individual is healthy, comfortable, and able to participate in or enjoy life events, e.g., Life satisfaction, Positive outlook towards life.
- Stigma in mental health: Negative or discriminatory attitudes/perception/behavior towards mental illness.
- Wellbeing: The state of being comfortable, healthy and happy.
- Psychopathology*: Psychopathological conditions.
- Population: The target population with mental health conditions
- Urban: Mental healthcare of urban population. Mental healthcare of population inhibiting in high density areas including urban morphology as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs.
- Rural: Mental healthcare of rural population. Mental Healthcare of a low population density and small settlements encompassing all population, housing, and territory not included within an urban area.
- Underprivileged: Mental healthcare of the underprivileged. Mental healthcare of populations that face barriers and challenges in accessing and using resources, due to geographic location, religion, sexual orientation, gendered-identity, racial, and ethnic populations.
- Indigenous: Mental healthcare of the indigenous community and individuals. Mental healthcare of people referred to as first people, aboriginal people, native people, or autochthonous people, are culturally distinct ethnic groups who are native to a place which has been colonized and settled by another ethnic group.
- Disabled: Mental healthcare of the disabled (physically and mentally disabled). Mental healthcare of people who have a physical or mental impairment, and the impairment has a substantial and long-term adverse effect on the person’s ability to carry out normal day-to-day activities.
- LGBT: Mental healthcare of individuals from LGBT community (lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender).
- Immigrants: Mental healthcare of people living permanently in a foreign country.
- Unit: The unit of mental healthcare.
- Adolescent: The period following the onset of puberty during which a young person develops/ transits between childhood and adulthood.
- Early (10-14): Early phase of adolescence which generally takes place between 10-14 years.
- Middle (15-17): Middle phase of adolescence which generally takes place between 15-17 years.
- Late (18-19): Later phase of adolescence which generally takes place between 18-19 years.
- Young Adulthood (20-24): The period of development between adolescent and adulthood which is generally between 20-24 years.
- Adolescent: The period following the onset of puberty during which a young person develops/ transits between childhood and adulthood.
- Setting/Provider: The setting /provider of mental healthcare.
- Institution: Institution involved in providing mental healthcare.
- Clinic: Health facility for outpatient care.
- Hospital: Public or private medical hospitals.
- School: An institution where instruction and learning is provided to the students.
- Professional: Professional mental health care provider/setting.
- Doctor/Physician: A person qualified to practice medicine.
- Psychologist: A mental health professional who specializes in psychology who is involved in prevention, study, and treatment of mental disorders.
- Mental health worker: Mental health professionals trained in psychology, psychotherapy/ counselling.
- Social worker: Professionals who aim to enhance overall well-being and help meet basic and complex needs of individuals and communities.
- Psychiatric nurse: A person formally educated and trained in the mental health care and who assists physicians during treatment.
- Educator: A professional engaged in sensitizing, training, and spreading awareness about mental health through education activities.
- Other: Other providers involved in mental healthcare and wellbeing.
- Parent: Parent (s) of the client/individual.
- Family: A social group made up of parents and their children.
- Friend: Peer(s) or friend(s) of the client/individual.
- Volunteer: A person who voluntarily undertakes or expresses a willingness to undertake a service
- Self: Individual self-availing mental healthcare.
- Digital /online: Technology or digital platform for mental healthcare e.g., tele-counselling, telemedicine.
Monad Map

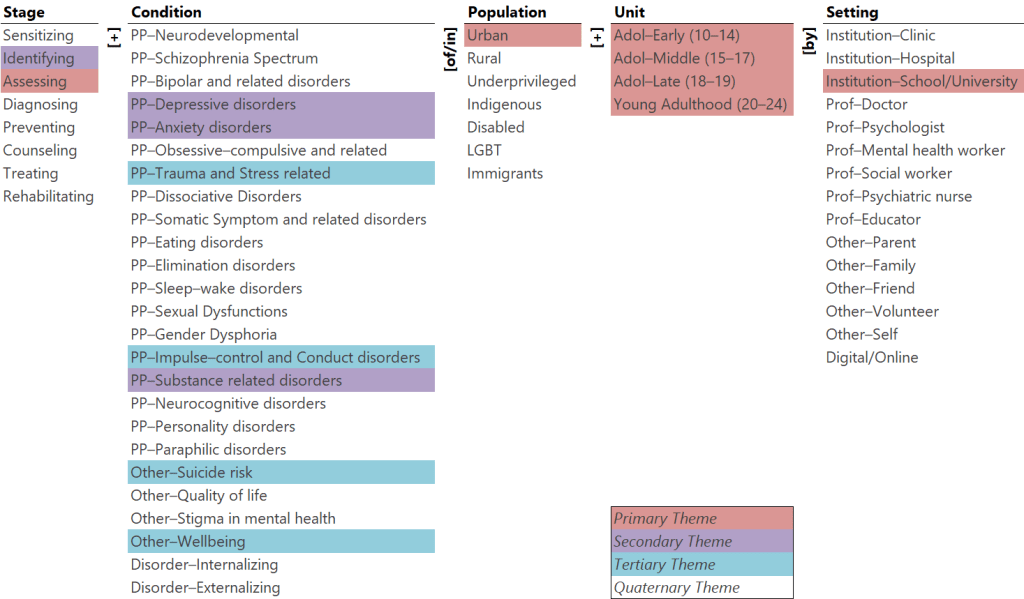
Theme Map
Related Links
State of Mental Health Research of Adolescents and Youth in Chile: An Ontological Analysis

Leave a comment