National healthcare policies of Australia, Chile, China, and India are analyzed using respective ontological frameworks to discover gaps.
Ontology of National Healthcare Policy in Australia
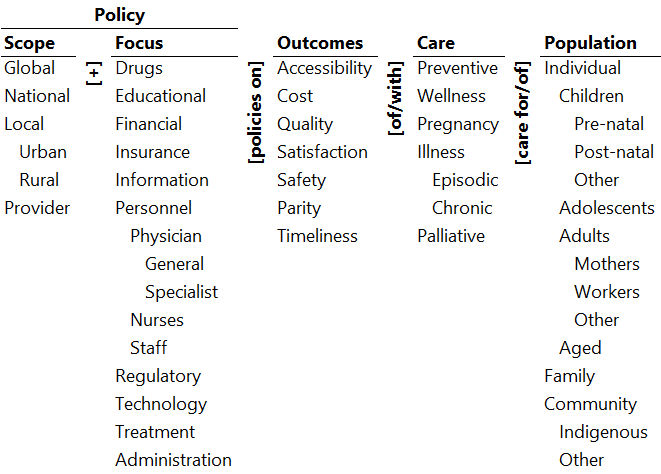
Ontology of National Healthcare Policy in Chile
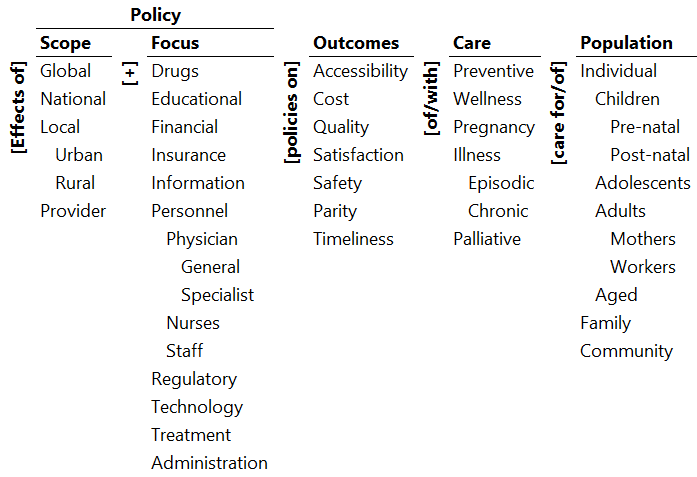
Ontology of National Healthcare Policy in China

Ontology of National Healthcare Policy in India
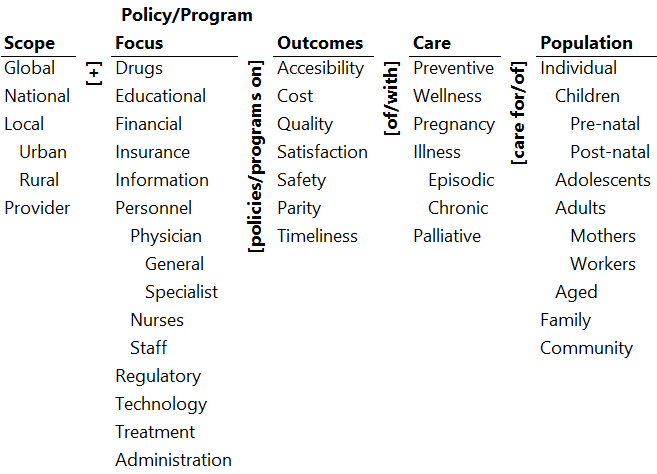
Illustrative Pathways
- National financial policies on accessibility of preventive care for family.
国家财政政策针对提高家庭预防性护理的可测性 - Local urban insurance policies on cost of palliative care for individual aged.
城市医保政策针对减少缓解老年人病痛的治疗费用 - Provider administration policies on cost of illness episodic care of individual adolescents.
服务提供者的行政管理政策针对减少青少年传染性疾病的治疗费用
Glossary
- Policy: Healthcare policy.
- Scope: Reach of the healthcare policy.
- Global: Policy applicable in all countries of the world.
- National: Policy applicable everywhere in China.
- Regional: Policy applicable to a region of China.
- Local: Policy applicable within a defined part of China.
- Urban: Policy applicable within local urban areas.
- Rural: Policy applicable within local rural areas.
- Provider: Policy applicable to a healthcare providing institution.
- Focus: Focus of the healthcare policy.
- Drugs: Policies regarding drugs used in healthcare.
- Food: Policies regarding food and nutrition in healthcare.
- Financial: Policies regarding healthcare finance.
- Legal: Policies regarding legal issues in healthcare.
- Insurance: Policies regarding healthcare insurance.
- Technology: Policies regarding healthcare technology.
- Information: Policies regarding healthcare information.
- Treatment: Policies regarding treatment.
- Personnel: Policies regarding healthcare personnel.
- Physician: Policies regarding physicians.
- General: Policies regarding general physicians.
- Specialist: Policies regarding specialist physicians.
- Nurses: Policies regarding healthcare nurses.
- Staff: Policies regarding healthcare staff.
- Physician: Policies regarding physicians.
- Administration: Policies regarding healthcare administration.
- Scope: Reach of the healthcare policy.
- Outcomes: The intended outcomes of healthcare policy.
- Accessibility: The accessibility of healthcare to the population.
- Cost: The cost of healthcare to the population.
- Quality: The quality of healthcare delivered to the population.
- Satisfaction: The population’s satisfaction with healthcare.
- Safety: The safety of healthcare delivered to the population.
- Parity: The parity of healthcare delivered to the population segments.
- Timeliness: The timeliness of healthcare delivery to the population.
- Care: The different types of healthcare.
- Preventive: Care to prevent illnesses and diseases in the population.
- Illness: Care of illnesses when they occur.
- Mental: Care of mental illness.
- Physiological: Treatment of physiological illness
- Episodic: Care during illness episodes — time bound.
- Chronic: Care of chronic illnesses — continuing.
- Occupational: Treatment of occupational illness.
- Palliative: Care to alleviate pain and suffering.
- Emergency: Care of emergency illness
- Population: The population targeted by the policy.
- Individual: Individual recipients of healthcare.
- Children: Children who are recipients of healthcare.
- Adolescents: Adolescents receiving healthcare.
- Adults: Adults receiving healthcare.
- Female: Women receiving healthcare.
- Pregnant women: Pregnant women receiving maternal healthcare.
- Workers: Workers receiving occupational/work related healthcare.
- Disabled: Disabled adults receiving healthcare.
- Other: Adults other than mothers and workers.
- Aged: Older people receiving elderly healthcare.
- Family: Family, as an entity, receiving healthcare.
- Community/group: Community/group as an entity receiving healthcare.
- Individual: Individual recipients of healthcare.
Related Links
Australia’s National Health Programs: An Ontological Mapping
National Healthcare Policies in Chile: An Ontological Meta-Analysis
China’s National Health Policies: An Ontological Analysis
National Healthcare Programs and Policies in India: An Ontological Analysis

Leave a comment