Mobile health or mHealth research has been growing exponentially in recent years. However, the research on mHealth has been ad-hoc and selective without a clear definition of the mHealth. Our ontological framework defines and maps the vast and complex domain of mHealth.
mHealth Ontology
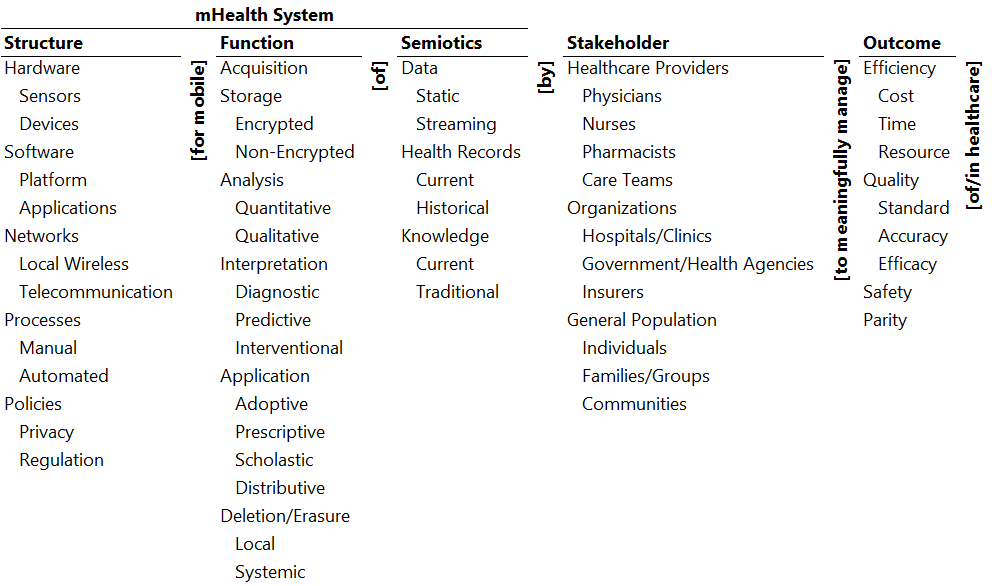
Illustrative Pathways
- Software for mobile interpretation of data by general population to meaningfully manage quality of healthcare. Example: Applications for tracking/flagging health data (e.g., fitness, blood pressure, glucose, etc.).
- Policies for mobile application of knowledge by organizations to meaningfully manage quality of healthcare. Example: Government regulatory control (e.g., FDA safety and innovation act), mHealth Regulatory Coalition guidelines.
- Processes manual for mobile deletion local of data static by healthcare providers physicians to meaningfully manage safety in healthcare. Example: Default expiration dates for patient data downloaded/entered/stored on mobile devices.
Glossary
- mHealth System: Mobile health system used to meaningfully manage healthcare.
- Structure: The structural elements of an mHealth system—the nouns describing the system.
- Hardware: The physical elements of the mHealth system.
- Sensors: Hardware used to measure and input a variety of data for healthcare.
- Devices: Hardware used to perform a variety of other information management functions in healthcare.
- Software: Computer programs used to manage healthcare information.
- Platform: The foundation for software such as an operating system.
- Application: Software used to perform a variety of other information management functions in healthcare.
- Networks: Wired and wireless connections for transfer of information.
- Local Wireless: Wireless networks with limited range, confined to a facility.
- Telecommunication: Wired and wireless connections with virtually unlimited range.
- Processes: Processes used by the stakeholders to manage information
- Manual: Processes handled almost entirely by people.
- Automated: Processes handled almost entirely by computers.
- Policies: Stakeholder rules guiding the management of information
- Privacy: Policies regarding privacy of information
- Regulation: Policies regulating the management of information.
- Hardware: The physical elements of the mHealth system.
- Function: The functions of the mHealth system—the verbs describing the behavior of the system.
- Acquisition: The function of obtaining information.
- Storage: The function of storing information.
- Encrypted: Storing the information with encryption to limit its readability.
- Non-Encrypted: Storing the information as is, without encryption, and hence directly readable.
- Analysis: Processing the information to discover relationships within.
- Quantitative: Processing of numerical information.
- Qualitative: Processing of non-numerical information.
- Interpretation: Discovering the meaning of relationships within the information.
- Diagnostic: The meaning of relationships for diagnosis.
- Predictive: The meaning of relationships for prediction.
- Interventional: The meaning of relationships for guiding intervention.
- Application: The use of the interpreted information.
- Adoptive: Translating the interpretation into action.
- Prescriptive: Prescribing action based on the interpretation.
- Scholastic: Using the interpretation for study or further analysis.
- Distributive: Propagating the interpretation to others.
- Deletion/Erasure: Removal of the information.
- Local: Removal of the information locally on a device.
- Systemic: Removal of the information everywhere.
- Semiotics: The transformation of symbols constituting the information.
- Data: The raw symbols—numerical, textual, graphical, etc.
- Static: Time invariant data, acquired and stored.
- Streaming: Time variant data, acquired in real time.
- Health Records: Organization of data to render healthcare.
- Current: Record of the current health data.
- Historical: Record of historical health data.
- Knowledge: Understanding of the logic of health and healthcare.
- Current: Current, on-the-point knowledge about health and/or healthcare.
- Traditional: Commonly accepted or evidence-based knowledge about health and /or healthcare.
- Data: The raw symbols—numerical, textual, graphical, etc.
- Structure: The structural elements of an mHealth system—the nouns describing the system.
- Stakeholder: Entity with a stake in healthcare.
- Healthcare Providers: Providers of healthcare.
- Physicians: Doctors in clinics and hospitals.
- Nurses: Nursing staff in clinics and hospitals.
- Pharmacists: Preparers/dispensers of pharmaceutical products in clinics, hospitals, and pharmacies.
- Care Teams: Teams of providers.
- Organizations: Organizational entities involved in the provision of healthcare.
- Hospitals/Clinics: Facilities of in-patient, out-patient, urgent, and ambulatory care.
- Government/Health Agencies: Entities regulating and providing auxiliary healthcare services.
- Insurers: Organizations providing insurance to healthcare recipients.
- General Population: The general recipients of healthcare.
- Individuals: Individual recipients of healthcare.
- Families/Groups: Recipient families or collections of individuals sharing some activity, interest or quality.
- Communities: Communities receiving healthcare.
- Healthcare Providers: Providers of healthcare.
- Outcome: The outcomes of healthcare
- Efficiency: The efficiency of healthcare delivery.
- Cost: The cost efficiency of healthcare delivery.
- Time: The time efficiency of healthcare delivery.
- Resource: The efficiency in terms of other resources like space, people, material, etc.
- Quality: The quality of healthcare.
- Standard: Quality of adherence to standards.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of diagnosis, treatment, etc. in healthcare.
- Efficacy: The success of care.
- Safety: The safety of recipients and providers of healthcare.
- Parity: The parity of healthcare delivered by the providers to the recipients.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of healthcare delivery.
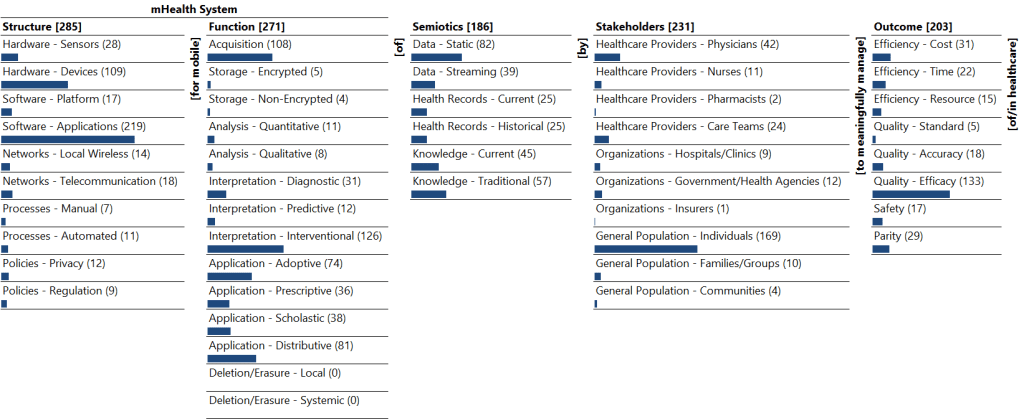
Monad Map

Leave a comment