eGovernment is a complex concept with multiple highly interconnected dimensions. The ontology of eGovernment captures all dimensions and elements of electronic government. The ontology is applied to identify gaps in research on local eGovernment.
Ontology
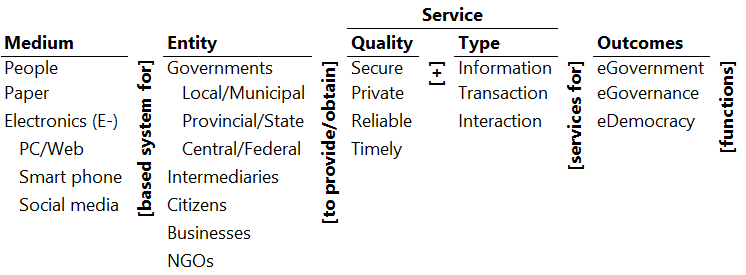
Illustrative Pathways
- People based system for governments to provide/obtain information services for eGovernment functions.
Example: Visiting the municipal office to obtain information on parking zones and restrictions from the clerk. - Paper based system for citizens to provide/obtain transaction services for eDemocracy functions.
Example: Voting with paper ballot. - Electronics based system for businesses to provide/obtain interaction services for eGovernance functions.
Example: Online discussion on new city tax policies. - Electronics social media based systems for citizens to provide/obtain information services for eGovernment services.
Example: Posting city office closure messages on Facebook.
Glossary
- Medium: The medium for providing government services.
- People: People based services.
- Paper: Paper forms, document services.
- Electronics (E-): Information technology-based services.
- PC/Web: Personal computer, worldwide web, internet based services.
- Smart phone: iPhone, Android, and other smart phone-based services.
- Social media: Facebook, Twitter, Yelp, and other social media-based services.
- Entity: The entity providing or receiving the government services.
- Governments The different levels of government.
- Local/Municipal: The lowest level of government.
- Provincial/State: The government of a province or state, above the local/municipal government.
- Central/Federal: The government of the country.
- Intermediaries: Organizations aiding the relationship with the government.
- Citizens: The citizens of the community governed by the local government.
- Businesses: Businesses within the community and having relationship with it at its government
- NGOs: Non-Government Organizations working with the community.
- Governments The different levels of government.
- Service: The types of services provided and received by the entities.
- Information: Providing and receiving information.
- Transaction: Exchange of funds, material, services, and information.
- Interaction: Continuing exchange of funds, material, services, and information.
- Outcomes: The outcome of government.
- eGovernment: Electronification of administrative functions.
- eGovernment: Electronification of government decision and policy making.
- eDemocracy: Electronification of political participation.
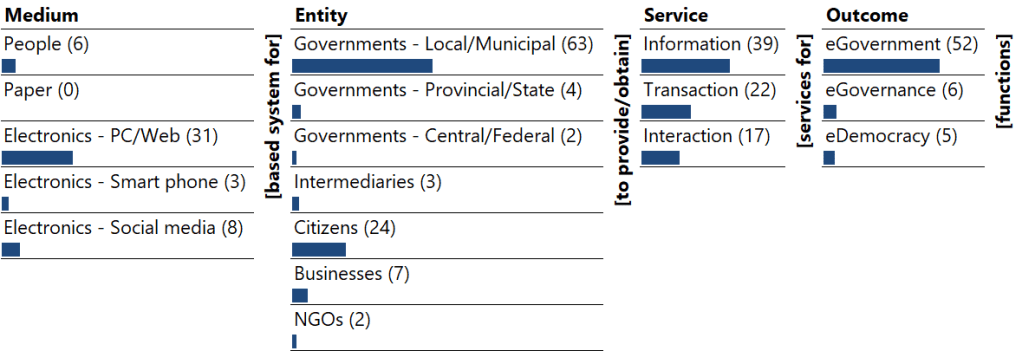
Monad Map

Leave a comment