The ontological framework captures the impacts of academic journals as described by the functions of these journals. The framework can also be adapted to capture the collective impact of articles published by an academic journal.
Ontology
Illustrative Pathways
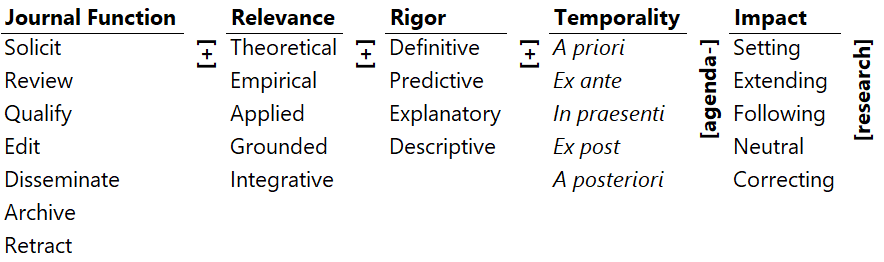
- Solicit theoretical definitive a priori agenda-setting research.
Example: A grand theory of technology acceptance. - Archive applied descriptive a posteriori agenda-neutral research.
Example: A repository of case studies. - Disseminate empirical predictive ex ante agenda-extending research.
Example: Replication of an empirical study in a different context. - Review empirical definitive ex post agenda-extending research.
Example: Review of a meta-analysis of research in a domain.
Glossary
- Journal Function
- Solicit: To solicit articles for publication.
- Review: To review the article for publication.
- Qualify: To assure the quality and fit of the article for publication.
- Edit: To edit the article style and presentation.
- Disseminate: To propagate the articles via different media.
- Archive: To store the articles for the future.
- Retract: To withdraw an article already published.
- Relevance:
- Theoretical: Logical theory construction, development, advancement, refinement.
- Empirical: Empirical testing of theories and consequent hypotheses and propositions.
- Applied: Theoretical and empirical application to a practical problem.
- Grounded: Theory development from grounded observations.
- Integrative: Integrative review/survey of theoretical/empirical research.
- Rigor:
- Definitive: Validation/invalidation of a definitive causal relationship.
- Predictive: Validation/invalidation of a predictive but not a causal relationship.
- Explanatory: Validation/invalidation of an association.
- Descriptive: Description of the entities, their structure, functions, and patterns.
- Temporality:
- A priori: Prior to the observation of a phenomenon.
- Ex ante: Prior to an event.
- In praesenti: During an event.
- Ex post: Following an event.
- A posteriori: After the observation of a phenomenon.
- Impact:
- Agenda-setting: Setting the agenda for future research.
- Agenda-extending: Extending the agenda of research through revisions and refinements.
- Agenda-following: Following the present agenda of research.
- Agenda-neutral: Idiosyncratic research not fitting any agenda.
- Agenda-correcting: Correcting errors in the present agenda of research.
Monad Map of MIS Journals

Monad Map of Information Systems Journal

Related Links
Impact Aspirations of MIS Journals: An Ontological Analysis
Twenty-Five Years of the Information Systems Journal: A Bibliometric and Ontological Overview

Leave a comment